

This could include a CT scan or MRI scan, which are pictures of the brain and arteries, a carotid ultrasound, which is a soundwave test of the carotid arteries which provide blood flow to the front parts of the brain, and blood tests. They will use several tests to help them figure out what type of stroke you're having and determine the best treatment for the stroke. Once you get to the hospital, your emergency team will review your symptoms and complete a physical exam. Don't wait to see if symptoms stop, for every minute counts. If you notice any of these, even if they come and go or disappear completely, seek emergency medical attention or call 911.
Now many strokes are not associated with headache, but a sudden and severe headache can sometimes occur with some types of stroke. Problems seeing in one or both eyes, trouble walking, and a loss of balance. Paralysis or numbness of the face, arm or leg on one side of the body. Look for these signs and symptoms if you think you or someone you know is having a stroke: Sudden trouble speaking and understanding what others are saying. Those who smoke, have high blood pressure or high cholesterol, have poorly controlled diabetes, suffer from obstructive sleep apnea, or have certain forms of heart disease are at greater risk as well. Being overweight, physically inactive, drinking alcohol heavily, recreational drug use. If you're 55 and older, if you're African-American, if you're a man, or if you have a family history of strokes or heart attacks, your chances of having a stroke are higher. So if you or someone you know is experiencing a stroke, you should call 911 and seek emergency medical care right away.Īnyone can have a stroke, but some things put you at higher risk.

Prompt treatment can reduce brain damage and the likelihood of death or disability. So the blood spills into the brain tissue or surrounding the brain. The second type of stroke happens when a blood vessel can leak or burst. In the first, a blocked artery can cut off blood to an area of the brain. They affect about 800,000 people in the United States each year.
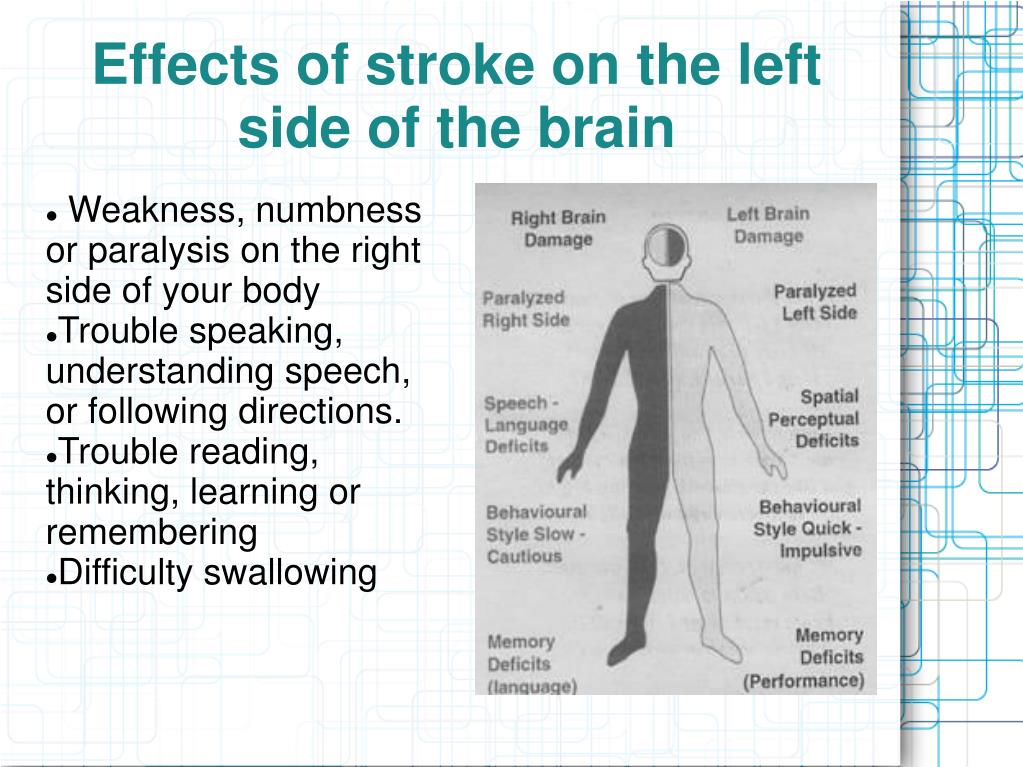
You've likely heard the term stroke before. Whether you're looking for answers for yourself or someone you love, we're here to give you the best information available. What is it, who it happens to, the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. In this video, we'll cover the basics of a stroke. Robert Brown, neurologist at Mayo Clinic.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
